MBR vs GPT, what’s that mean?
When you initialize your disk, you will be asked which partition style to choose, MBR or GPT. For most users, they are not clear about this concept. Now I will explain to you in detail what MBR and GPT are. Here, you will learn the difference between MBR vs GPT, and how to make a safe conversion between MBR and GPT without losing data.
-
What is MBR?
MBR, short for Master Boot Record, is a traditional partitioning scheme used in older computers and operating systems. It is located in the first sector of the disk and contains essential boot information, such as the partition table and the boot loader. MBR supports up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition.
However, MBR has certain limitations. It can only address disks up to 2 terabytes (TB) in size, and it relies on the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) to boot the operating system. Additionally, MBR does not provide built-in redundancy or error correction.
-
What is GPT?
GPT, which stands for GUID Partition Table, is a newer partitioning scheme introduced with the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) system. GPT offers several advantages over MBR. It supports disks larger than 2 TB and can handle up to 128 primary partitions. GPT also includes a backup partition table, ensuring data redundancy and reducing the risk of data loss.
GPT disks use a globally unique identifier (GUID) to identify partitions, allowing for a more flexible and efficient disk management system. It is compatible with both BIOS and UEFI systems, making it more versatile compared to MBR.
What are the differences between MBR and GPT?
After understanding what MBR and GPT are, we need to figure out what exactly is the difference between them.
-
Partitioning scheme:
MBR uses a traditional partitioning scheme with a limited number of primary partitions.
GPT employs a modern partitioning scheme that allows for a higher number of primary partitions.
-
Disk capacity support:
MBR supports disks up to 2 TB in size.
GPT can handle disks larger than 2 TB.
-
Compatibility:
MBR is compatible with both BIOS and UEFI systems.
GPT is compatible with both BIOS and UEFI systems, providing more versatility.
-
Boot process:
MBR relies on the BIOS for booting the operating system.
GPT uses the UEFI system for booting, which offers faster startup times and more advanced features.
-
Data recovery:
MBR has a higher chance of data corruption due to its limited error-checking capabilities.
GPT includes a backup partition table, reducing the risk of data loss and improving data recovery options.
In general, GPT is the more popular partitioning style nowadays because GPT disks have more memory and are more secure. Also, Windows 11 only supports the GPT disk as a boot disk.
How to convert MBR to GPT without losing data
When initializing a hard drive, you can set the partition style to GPT. If you already have an MBR disk, how do you convert it to GPT? Disk Management is probably the first choice for most people, but it can only convert empty disks, which means you have to delete all the partitions on that disk, which will make you lose data!
AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional is a powerful Windows partition manager designed to help users efficiently manage their disk partitions. It offers a wide range of features and tools that enable users to resize, move, merge, split, and convert partitions with ease. One notable feature of AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional is its “Convert to GPT” function.
Here are some key points to know about the “Convert to GPT” function:
- Easy Conversion Process: AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional simplifies the process of converting MBR to GPT. With just a few clicks, you can initiate the conversion and let the software handle the rest.
- Data Integrity: During the conversion process, AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional ensures the integrity and safety of your data. It performs a thorough analysis of the disk and its partitions, preserving all existing data without the risk of loss or corruption.
- Boot Mode Compatibility: The “Convert to GPT” function supports both BIOS and UEFI boot modes, making it compatible with a wide range of systems. This allows you to convert your disk to GPT regardless of your system’s boot mode.
- Partition Alignment: AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional automatically aligns the partitions after the conversion to GPT. Proper partition alignment helps optimize disk performance and ensures the smooth operation of the system.
- Additional Disk Management Features: Apart from the “Convert to GPT” function, AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional offers a comprehensive suite of disk management tools. You can perform tasks such as migrating Windows 10 to SSD, disk/partition copy, disk/partition wiping, and more, all from a user-friendly interface.
By utilizing the “Convert to GPT” function in AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional, you can unlock the full potential of GPT partitioning on your disk, enabling support for larger capacities and taking advantage of the advanced features offered by GPT.
Step 1. Right-click the MBR disk and choose Convert to GPT.
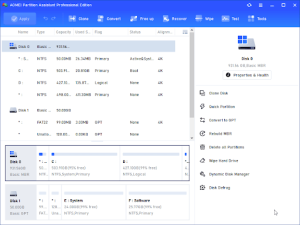
Step 2. You’ll be asked that “Are you sure to convert the selected disk from MBR to GPT disk?”. Click OK.

Step 3. To commit operation, please click Apply.

Did you see it? This is the whole process to convert MBR to GPT with AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional. You only need three steps to convert your disks and you won’t lose any data. If you are looking for a way to convert MBR to GPT, you shouldn’t miss it.
Final Thoughts
The choice between MBR and GPT partition styles depends on the specific needs and requirements of your computer system. While MBR is the older and more limited option, GPT offers advantages such as support for larger disks, increased partition capacity, data redundancy, and compatibility with both BIOS and UEFI systems. Consider your disk size, partitioning needs, and the capabilities of your system. When selecting MBR VS GPT for safe and efficient disk initialization.